What is the structure and working principle of the brake wheel cylinder?
Oct 11, 2025
What is the structure and working principle of the brake wheel cylinder?
Brake Wheel Cylinder Structure
The brake wheel cylinder, as the core actuator of the braking system, plays a vital role in ensuring stable braking performance. A High quality brake wheel cylinder not only enhances braking efficiency but also extends the lifespan of other related components. It mainly consists of the following parts:
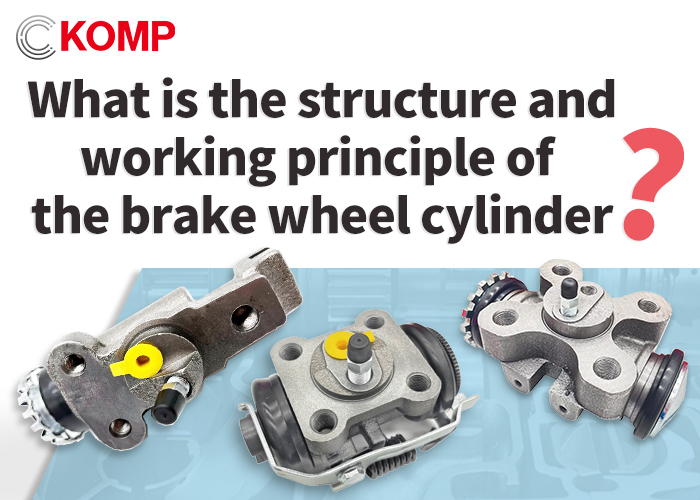 1. Piston: A hydraulically or pneumatically driven mechanical component that directly pushes the brake pads against the brake disc/drum.
2. Sealing System: This includes the cup, seal, and dust cover to prevent fluid leakage and dust intrusion. Jamming is often caused by a damaged dust cover.
3. Guide Pin: Ensures parallel movement of the brake pads. Uneven wear is often caused by insufficient lubrication or corrosion on the guide pins.
4. Oil/Air Line: Cars use hydraulic oil to transmit pressure, while trucks rely on compressed air.
As a professional brake wheel cylinder manufacturer, we understand that every detail of the cylinder design—such as sealing performance, piston material, and surface treatment—directly affects braking safety and reliability.
Working Principle
1. Hydraulic System (Cars/Electric Vehicles)
Braking Process: When the pedal is pressed, the master cylinder pressurizes the hydraulic oil, pushing the wheel cylinder piston outward, causing the brake pads to clamp against the brake disc.
Return Mechanism: When the pedal is released, the piston returns to its original position under the action of the return spring, releasing the brake pads from the disc.
2. Pneumatic System (Trucks/Buses)
Service Brake: High-pressure air enters the wheel cylinder through the air pipe, pushing the diaphragm and driving the camshaft to open the brake pads.
Parking Brake: The air brake uses spring force to force the piston out, achieving mechanical locking.
Special Design Types
1. Bidirectional Assisted Balanced Type: Automatically increases braking force in both forward and reverse, with clearance adjusted by a toothed nut.
2. Integrated Parking Brake wheel Cylinder: Integrated hydraulic piston and mechanical cable ensure mechanical braking through the parking brake even if hydraulic pressure fails.
Many Hot Sale brake wheel cylinder models in the market now integrate these functions to meet different vehicle applications, improving both safety and versatility.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
1. Regular Inspection: Clean and lubricate the guide pins to prevent uneven wear of the brake pads.
2. Dust Protection: Check the integrity of the dust cover to prevent rust and seizure of the piston.
3. System Venting: Bleed the hydraulic system and check the air system for leaks.
Common Problems
1. Uneven Brake Pad Wear: Often caused by stuck guide pins or poor return of the wheel cylinder piston.
2. Decreased Braking Force: This may be due to seal failure or pipe leakage, and requires prompt repair.
1. Piston: A hydraulically or pneumatically driven mechanical component that directly pushes the brake pads against the brake disc/drum.
2. Sealing System: This includes the cup, seal, and dust cover to prevent fluid leakage and dust intrusion. Jamming is often caused by a damaged dust cover.
3. Guide Pin: Ensures parallel movement of the brake pads. Uneven wear is often caused by insufficient lubrication or corrosion on the guide pins.
4. Oil/Air Line: Cars use hydraulic oil to transmit pressure, while trucks rely on compressed air.
As a professional brake wheel cylinder manufacturer, we understand that every detail of the cylinder design—such as sealing performance, piston material, and surface treatment—directly affects braking safety and reliability.
Working Principle
1. Hydraulic System (Cars/Electric Vehicles)
Braking Process: When the pedal is pressed, the master cylinder pressurizes the hydraulic oil, pushing the wheel cylinder piston outward, causing the brake pads to clamp against the brake disc.
Return Mechanism: When the pedal is released, the piston returns to its original position under the action of the return spring, releasing the brake pads from the disc.
2. Pneumatic System (Trucks/Buses)
Service Brake: High-pressure air enters the wheel cylinder through the air pipe, pushing the diaphragm and driving the camshaft to open the brake pads.
Parking Brake: The air brake uses spring force to force the piston out, achieving mechanical locking.
Special Design Types
1. Bidirectional Assisted Balanced Type: Automatically increases braking force in both forward and reverse, with clearance adjusted by a toothed nut.
2. Integrated Parking Brake wheel Cylinder: Integrated hydraulic piston and mechanical cable ensure mechanical braking through the parking brake even if hydraulic pressure fails.
Many Hot Sale brake wheel cylinder models in the market now integrate these functions to meet different vehicle applications, improving both safety and versatility.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
1. Regular Inspection: Clean and lubricate the guide pins to prevent uneven wear of the brake pads.
2. Dust Protection: Check the integrity of the dust cover to prevent rust and seizure of the piston.
3. System Venting: Bleed the hydraulic system and check the air system for leaks.
Common Problems
1. Uneven Brake Pad Wear: Often caused by stuck guide pins or poor return of the wheel cylinder piston.
2. Decreased Braking Force: This may be due to seal failure or pipe leakage, and requires prompt repair.
