In the automotive world, the brake system plays a crucial role in ensuring safety on the roads. At the heart of this system lies the brake master cylinder, a key component responsible for converting the driver's input into hydraulic pressure that activates the braking mechanism. This blog post aims to explore the working principle and classification of the brake master cylinder, shedding light on its vital role in vehicle braking systems.


Working Principle:
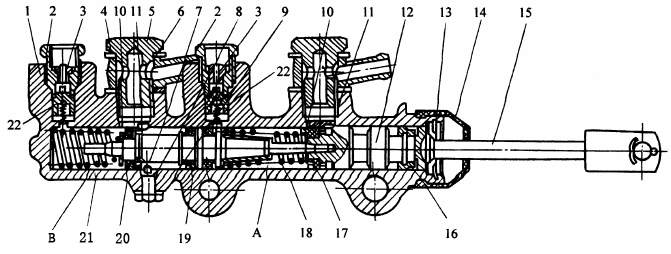
The brake master cylinder functions based on the principle of hydraulic
pressure amplification. When the driver applies force to the brake pedal, a
piston inside the master cylinder is pushed forward, compressing the brake
fluid within the cylinder. This compression creates hydraulic pressure, which
is then transmitted to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders, resulting in the
application of the brakes.
Internal Components:
The brake master cylinder comprises several essential components, including a
reservoir, piston, primary and secondary chambers, and seals. The reservoir
stores the brake fluid, allowing it to be replenished as necessary. The piston
serves as the main actuator, converting the linear motion from the brake pedal
into hydraulic pressure. The primary and secondary chambers regulate the
distribution of hydraulic pressure to different brake circuits, ensuring
balanced braking. Seals prevent any leakage and maintain the integrity of the
system.
Classification:
1. Single-Circuit Master Cylinder:
This type of master cylinder has a single chamber and is commonly used in older
vehicles or simpler brake systems. In case of a failure in the brake system,
such as a leak or loss of hydraulic pressure, the entire braking system becomes
compromised. Therefore, this design is considered less safe and is now rarely
used in modern vehicles.
2. Dual-Circuit Master Cylinder:
Dual-circuit master cylinders feature two separate chambers that supply
hydraulic pressure to two independent braking circuits, usually the front and
rear brakes. This design enhances safety by providing redundancy. If one
circuit fails, the other circuit can still operate, ensuring partial braking
capability. Most modern vehicles are equipped with dual-circuit master
cylinders.
3. Tandem Master Cylinder:
Tandem master cylinders are similar to dual-circuit master cylinders but with
an additional safety feature. They consist of two separate pistons, each
operating its own braking circuit. This design increases safety by providing
independent control over the front and rear brakes and ensures proper braking
in case of a failure in one circuit.
(Image-source-network)
Conclusion:
The brake master cylinder is a vital component in the automotive braking
system, responsible for converting mechanical force into hydraulic pressure.
Understanding its working principle and classification helps us appreciate the
importance of this component in ensuring safe and reliable braking. With the
advancements in automotive technology, the dual-circuit and tandem master
cylinders have become standard, providing enhanced safety features and
improving the overall braking performance of modern vehicles.

